Euthanasia Explained: Understanding the Ethics and Legality of Mercy Killing

Euthanasia, frequently known as “mercy killing,” is the exercise of intentionally finishing someone’s existence to relieve them of ache and struggling, normally due to an incurable or terminal contamination. It is a particularly sensitive, moral, and prison trouble that has sparked debates globally. The time period derives from the Greek phrases european (desirable) and thanatos (death), that means “correct demise.”

Types of Euthanasia
Euthanasia may be classified into several kinds primarily based at the patient’s consent and the approach of administering it:
1. Voluntary Euthanasia:
In this form, the affected person explicitly requests help in ending their lifestyles. Voluntary euthanasia is prison in some nations, like Belgium, the Netherlands, and parts of the United States (including Oregon).
2. Non-Voluntary Euthanasia:
This occurs while the patient is not able to provide consent (as an example, if they are in a coma or affected by extreme brain damage). In such cases, a decision is made on their behalf, typically by using near family participants or criminal representatives, based on the patient’s presumed needs or best hobby.
3. Involuntary Euthanasia:
In this case, euthanasia is done with out the affected person’s consent and in opposition to their will. This is commonly considered homicide in maximum felony systems and is not part of the criminal debates round euthanasia.
4. Active Euthanasia:
This involves immediately causing the demise of a patient, regularly via administering a deadly substance along with a drug injection. Active euthanasia is more arguable because of its direct involvement in inflicting death.
5. Passive Euthanasia:
Passive euthanasia involves withholding or retreating life-maintaining treatments, consisting of ventilators or feeding tubes, permitting the affected person to die naturally from their contamination.
Legal Status of Euthanasia
The legality of euthanasia varies extensively by means of country:
Legalized Euthanasia:
Countries like the Netherlands, Belgium, Luxembourg, and Canada have legalized voluntary lively euthanasia under strict guidelines. In the U.S., sure states which includes Oregon and Washington permit doctor-assisted suicide, wherein a doctor prescribes a lethal dose of medicine, which the affected person administers themselves.
Prohibited Euthanasia:
In many other nations, euthanasia remains unlawful, with stiff penalties for those who help inside the system. For instance, inside the United Kingdom and most of the United States, euthanasia is illegal, although a few forms of passive euthanasia, like withdrawing life help, may be legally allowed underneath positive occasions.
Ethical Considerations
Euthanasia increases several moral troubles:
1. Autonomy and the Right to Die:
Supporters argue that people have the right to pick out how and when they die, particularly while going through insufferable suffering from terminal situations.
2. Medical Ethics and the Hippocratic Oath:
Critics argue that euthanasia conflicts with a physician’s ethical obligation to “do no harm,” as outlined inside the Hippocratic Oath. Therefore, a few medical doctors view euthanasia as incompatible with their obligation of care.
3. Slippery Slope Argument:
Another difficulty is that legalizing euthanasia ought to cause a “slippery slope,” where the practice may be extended to non-terminally sick sufferers or people with disabilities, elevating concerns about abuse or devaluing human life.
4. Religious Perspectives:
Many religious traditions, in particular in Christianity, Islam, and Judaism, oppose euthanasia, viewing life as sacred and best God having the right to end it.
5. Dignity in Death:
Proponents frequently argue that euthanasia allows for a greater dignified dying, unfastened from extended suffering and loss of bodily autonomy. They emphasize that present day medicine can sometimes extend life artificially, resulting in unnecessary pain or indignity.
Methods of Euthanasia
The procedure and methods of euthanasia can range depending on legal, scientific, and ethical issues:
Lethal Injection:
This is the maximum common technique in jurisdictions in which active euthanasia is legal. It includes the administration of medicine that first render the patient subconscious after which result in loss of life, typically thru cardiac arrest or breathing failure.
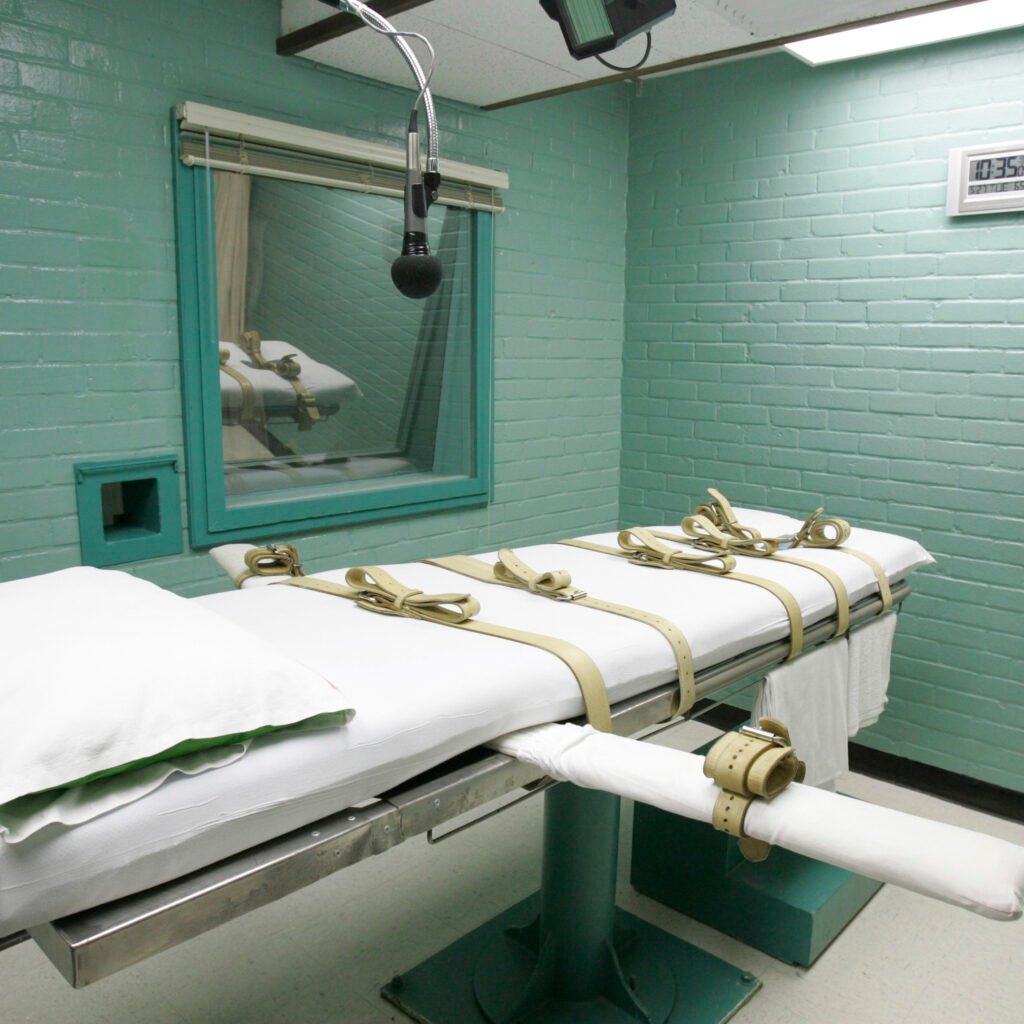
Sedation and Withdrawal of Treatment:
In passive euthanasia, the affected person can be heavily sedated and lifestyles-helping measures along with feeding tubes or ventilators are discontinued. The patient typically dies from the underlying illness.
Physician-Assisted Suicide (PAS)
Euthanasia: The medical doctor at once administers a existence-finishing substance.
Physician-Assisted Suicide (PAS): The patient administers the substance themselves, with a doctor’s guidance and prescription.
Countries and Regions with Legalized Euthanasia and PAS
Netherlands: One of the primary international locations to legalize euthanasia (2002), beneath strict conditions.
Belgium: Allows euthanasia for adults and minors (below certain conditions), expanding their laws in latest years.
Switzerland: Known for legalizing assisted suicide, regularly attracting global sufferers.
Canada: Legalized euthanasia in 2016 underneath Medical Assistance in Dying (MAID).
United States: In states like Oregon and Washington, PAS is prison.
Conclusion
Euthanasia is a complicated and multifaceted problem that intertwines prison, moral, scientific, and spiritual issues. While some view it as a compassionate reaction to cease suffering, others see it as a morally and ethically tricky exercise. The communication continues to evolve globally, with nations and states grappling with the way to balance individual autonomy, clinical ethics, and the sanctity of existence.








